5 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis most common mechanism Inhibition of Protein Synthesis Translation second. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
11 7 Mechanisms For Resistance Biology Libretexts
Streptococcus pyogenes or group A streptococcus is a major human pathogen that causes over 600 million infections annually Lynskey Lawrenson Sriskandan 2011.

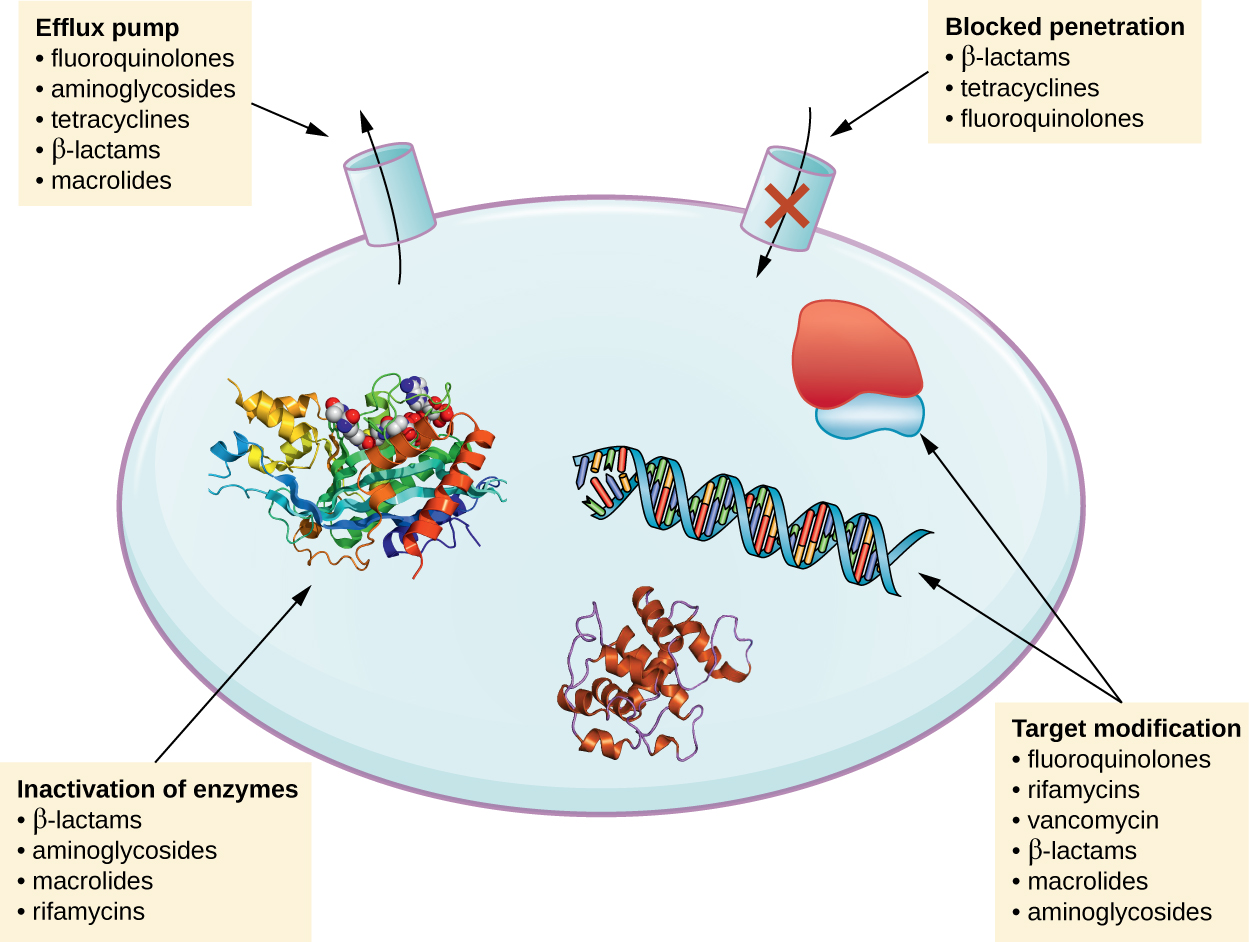
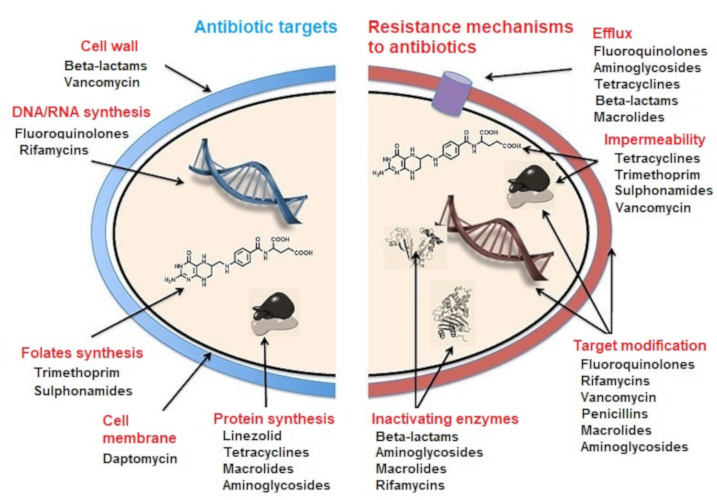
. These are production of drug-inactivating enzymes modification of an existing target acquisition of a. The antimicrobial resistance is recognized as a major problem in the treatment of microbial infections. The biochemical resistance mechanisms used by bacteria include the following.
In this case the mutations in the msbA gene might be related to antibiotic resistance. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance Front Microbiol. The biochemical resistance mechanisms used by bacteria include the following.
Inactivation of a drug like penicillin an enzyme that cleaves a portion of molecule and renders it inactive. Five Basic Mechanisms of Antibiotic Action against Bacterial Cells. 3Altered target site such that the antibiotic can no longer bind to the target.
A growing number of infections such as pneumonia. Intrinsic resistance may make use of limiting uptake drug inactivation and drug efflux. Acquired resistance mechanisms used may be drug target modification drug.
This module aims to introduce the microbiological aspects of antimicrobial resistance. The treatment of bacterial infections is increasingly complicated by the ability of bacteria to develop resistance to antimicrobial agents. The three fundamental mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance are 1 enzymatic degradation of antibacterial drugs 2 alteration of bacterial proteins that are antimicrobial targets and 3.
As early as the last century scientists have realized that metal resistance genes are. The receptor that transports the drug is altered so the drug. 1Enzymatic inactiavtion of antibiotic.
Antibiotic inactivation target modification altered permeability and bypass of metabolic pathway. The three fundamental mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance are 1 enzymatic degradation of antibacterial drugs 2 alteration of bacterial proteins that are antimicrobial. Antimicrobial agents are often categorized.
2Antibiotic efflux pumps get the antibiotic out of the cell. Antibiotic resistance occurs naturally but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process. By the end of the module you will be able to.
Acquired antimicrobial resistance generally can be ascribed to one of five mechanisms.

Mechanisms Of Antibiotic Resistance There Are Three Main Ways By Which Download Scientific Diagram

Emergence And Spread Of Antibiotic Resistance Part 2 React

Microbiology Antimicrobial Resistance Learning Site
Antibiotics Antibiotic Resistance And Environment Encyclopedia Of The Environment
0 Response to "5 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance"
Post a Comment